An intro to Argo CD
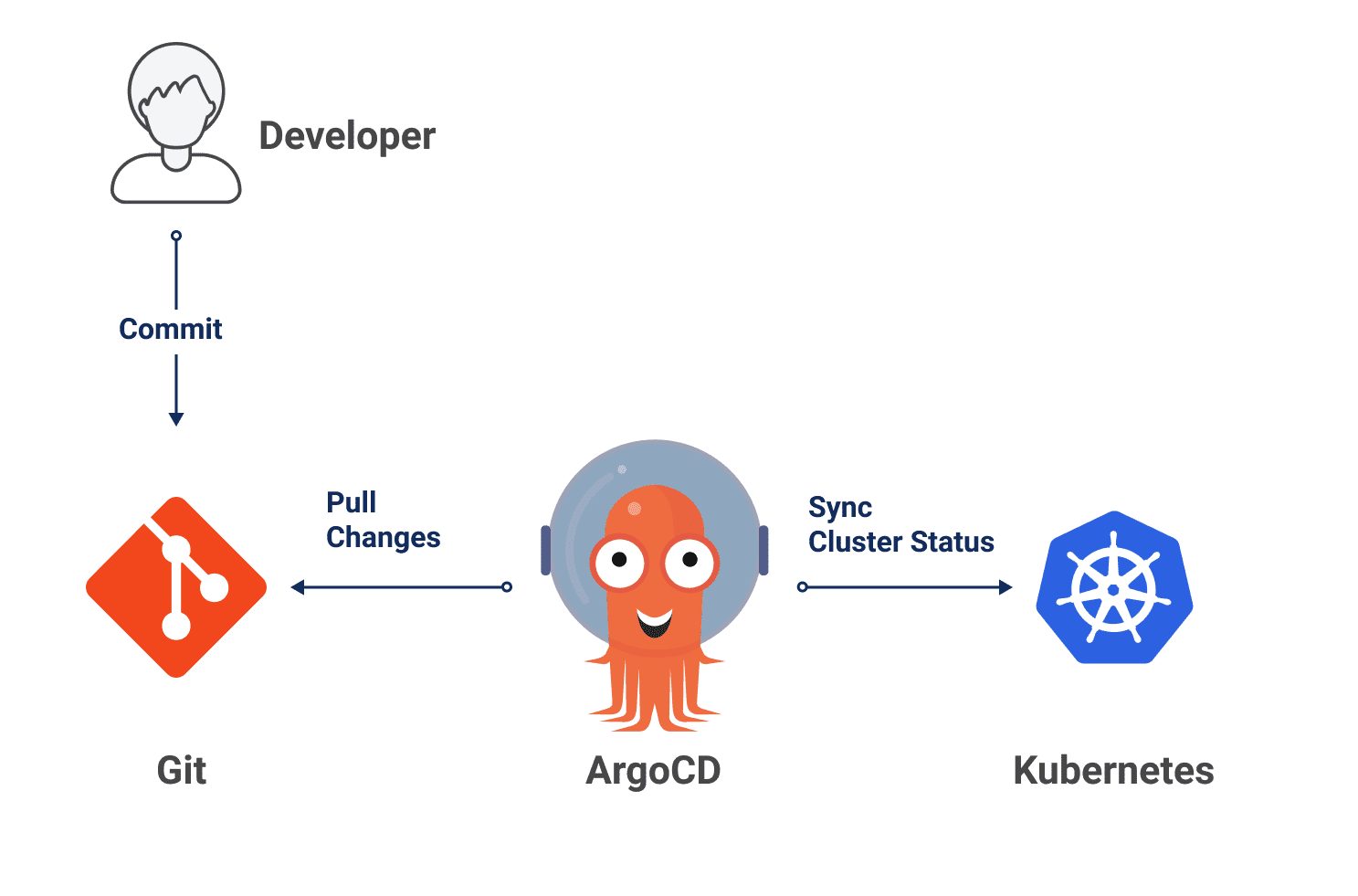
Argo CD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes. The core idea of GitOps is having a Git repository that always contains declarative descriptions of the infrastructure currently desired in the production environment, and an automated process to make the production environment match the described state in the repository. Argo CD follows the GitOps pattern of using Git repositories as the source of truth for defining the desired application state. It is implemented as a kubernetes controller which continuously monitors running applications, and compares the current live state against the desired target state (as specified in the Git repo).Any modifications made to the desired target state in the Git repo can be automatically applied, and reflected in the specified target environments.
Difference with other CD pipelines
Argo CD, in contrast to push-based CD solutions, is able to detect changes in the project, and deploy it to Kubernetes. By using the push method, deployments to the cluster are initiated by an external system (often CD pipelines) following the successful completion of a prior CI pipeline or the commit to a git repository. In this method, the cluster is accessible to the pipeline system. With pull-based systems, there is an operator inside the cluster that periodically monitors the related git repositories, and docker registries; if a change is detected, the cluster state is changed from within. Due to the fact that no external client possesses credentials that grant admin access to the cluster, this technique is widely regarded as being very secure.
How to get Started with Argo CD?
The minimum requirement to get started using argo CD is an application custom resource definition (CRD). The Application CRD is the Kubernetes resource object representing a deployed application instance in an environment. It is defined by two key pieces of information:
-
Source reference to the desired state in Git (repository, revision, path, environment)
-
Destination reference to the target cluster, and namespace.
Example
This example assumes that you’re familiar with core Git, Docker, Kubernetes, and Continuous Delivery. In addition, you must have minikube configured locally. You can create your own docker image or use the docker mentioned in the example.
We first need to install Argo CD. The most common way is to use kubectl command.
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/core-install.yamlsecondly, We need to create a kubernetes deployment ,and service file, then push it on out git repo.
Deployment File
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: luna-deployment
labels:
app: luna
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: luna
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: luna
spec:
containers:
- name: spring-boot-app
image: natanstb/gs-spring-boot-docker
ports:
- containerPort: 3000Service File
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-app-service
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 3000
targetPort: 3000
nodePort: 30004
selector:
app: lunaWe then create Argo CD application file which points to the git repo we just created
Application CRD
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: luna-app
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/tesfayenati/argo-cd-example
targetRevision: HEAD
path: dev
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: myapp
syncPolicy:
automated:
selfHeal: true
prune: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=trueLastly, apply application CRD using
kubectl apply -n argocd -f application.yamlWe just need to verify the created kubernetes resource using kubectl get pods command, and using kubectl get svc to check the services created.
For fetching the minikube IP, and a service’s Node port we can use:
minikube service my-app-service --urlArgo CD also comes with A UI which makes it suitable to visualize deployment processes. It can be accessed locally by port forwarding. To access the admin UI, we can
-
First we get the decoded password using:
kubectl -n argocd get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d
-
Port forwarding using:
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:443-
Then browse https://localost:8080
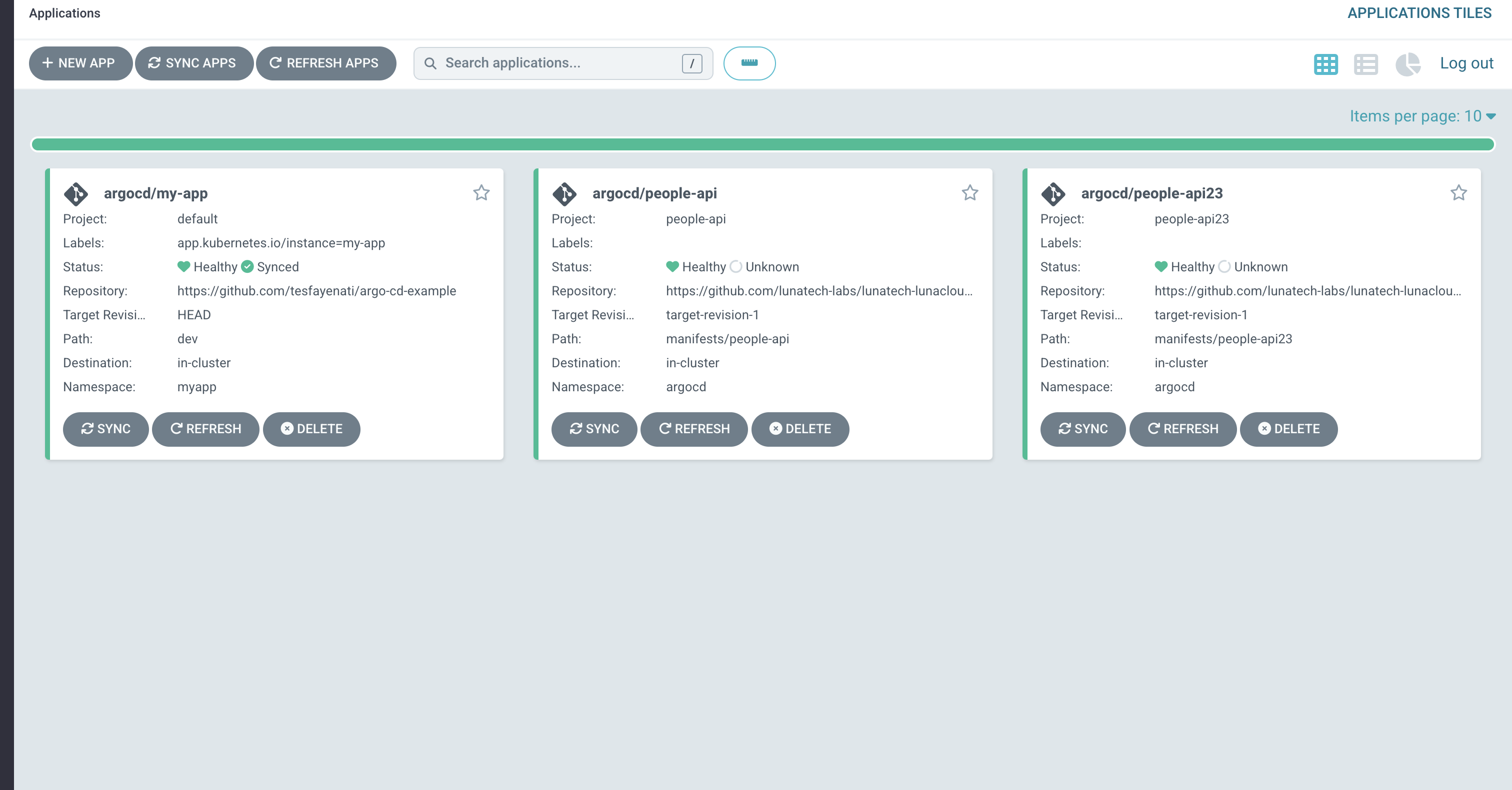
This was a short Introduction to Argo CD, which makes deployment process faster, and safer.
